Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation helps you effectively manage and respond to feelings, ensuring balanced reactions. With AERCS, you’ll gain control, improve relationships, and enhance overall well-being.
Manage Emotions Effectively
Improve Personal Relationships
Enhance Overall Well-Being
Reduce Anger and Anxiety
Unlock Hope and Healing with a Complimentary 20-Minute Phone Call Consultation
Are you ready to take the first step towards a brighter future? At AERCS, we're here to support you on your path to well-being. Our complimentary intake call is your opportunity to connect with us, confidentially share your journey, and discover the transformative support we offer. By taking this call, you're not just talking; you're taking control of your well-being, paving the way for tailored therapy that can change your life. Don't wait—book your call today and embrace the healing journey that awaits you.
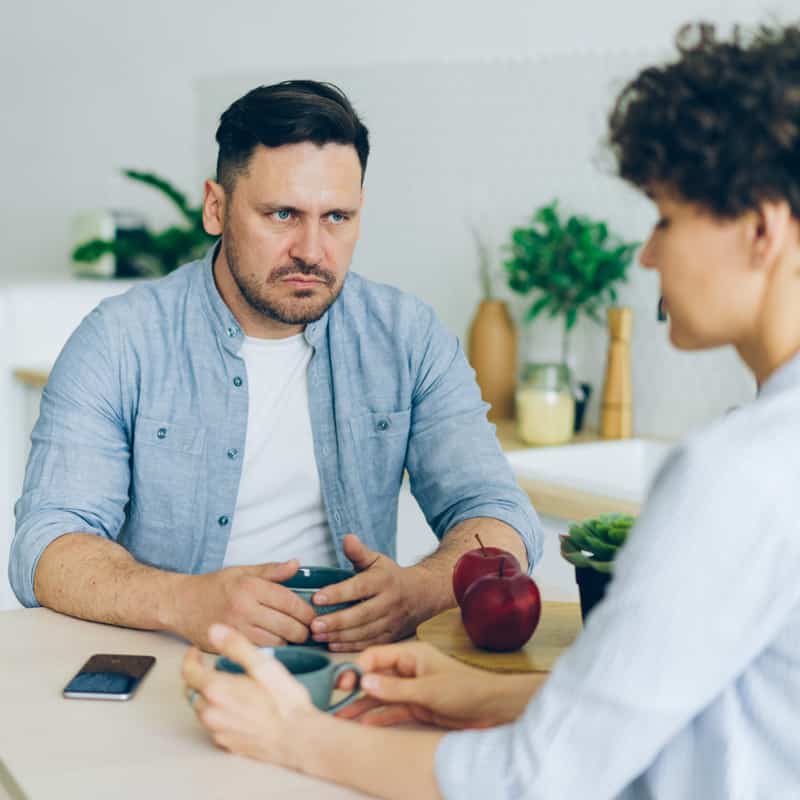

AERCS’ certified counsellors help people address their emotional regulation challenges.
AERCS’ staff includes registered counsellors, psychotherapists, and certified social workers, helping couples with:
- Managing Emotional Experiences
- Separating Emotions From Thoughts and Actions
- Rethinking Difficult Situations
- Reducing Anger and Anxiety
- Hiding Sadness or Fear
- Coping With Physical Changes Affecting Emotions
- Focusing on Reasons for Happiness or Calm
- Understanding Intense Emotional Peaks and Valleys
- Addressing Rapidly Changing Emotions
- Recognizing Triggers From Past Negative Situations
What is Emotional Regulation?

Emotional regulation is a term used to describe a person’s ability to manage emotional experiences. Most people can easily regulate their emotions as necessary throughout the day, but there are some among us that lack the ability to separate their emotions from their thoughts and actions.
Overcoming emotional instability may involve learning new behaviors such as rethinking difficult situations to reduce anger or anxiety, hiding sadness or fear, or focusing on reasons to feel happy or calm.
Emotions are an everyday part of life. Most of us feel happy if we win something, and sad if we lose out. We miss our loved ones and can get angry or express disappointment when someone lets us down. While we deal with these emotions naturally, some people have more volatile feelings and may experience more profound joy and deeper sadness. These peaks and valleys impact their lives and the people around them.
Individuals who experience intense emotions may find themselves calm one moment and then loud and angry the next. Their rapidly changing emotions causes them to do and say things they regret. Over time their anger can permanently damage relationships and hurt their credibility.
If you have questions, or need to speak to someone, you can contact AERCS at any one of our locations:
Why am I always so emotional?
Some individuals are genetically predisposed to rapid changes of emotion, and some simply never learned good emotional regulation. In other cases, people lose control when they experience triggers for negative situations that happened in their past. There can also be physical changes that cause a person to lose control of their emotions, such as exhaustion or a drop in blood sugar.
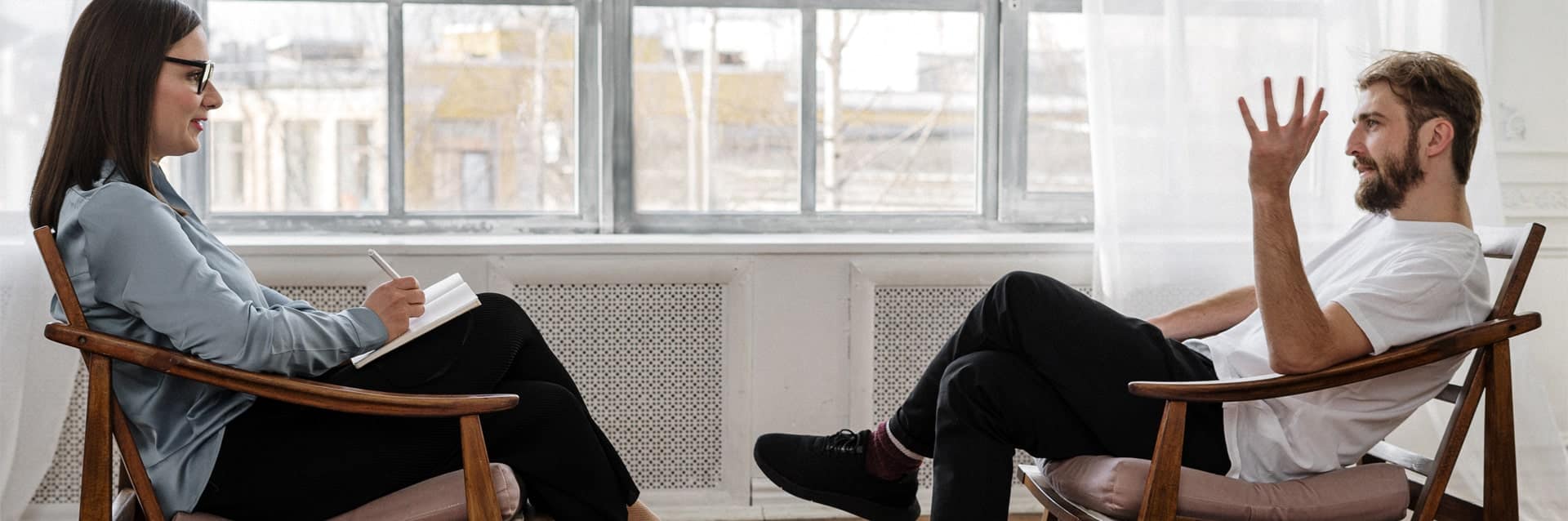

Emotional dysregulation refers to poorly regulated emotional responses that are not within a range of typically accepted emotional reactions.
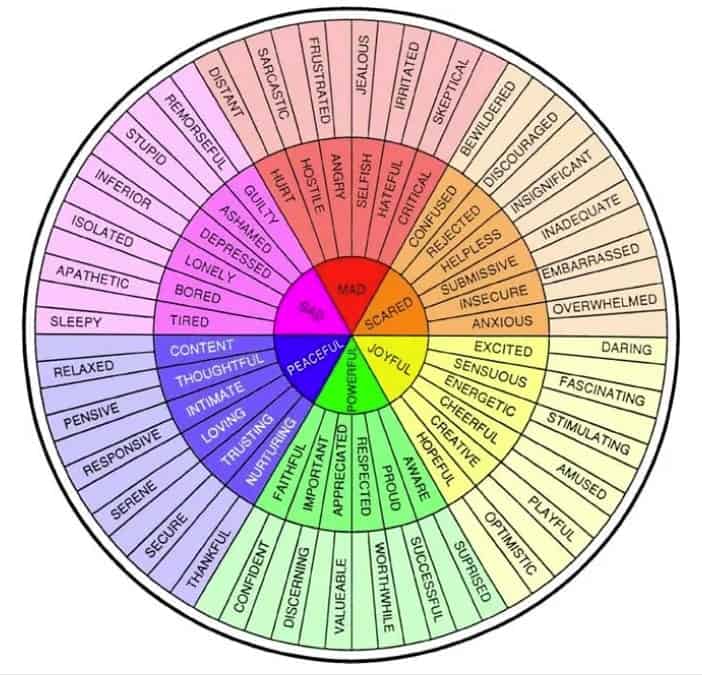
Dysregulation can also refer to significant mood swings, significant changes in mood, or emotional lability. It can involve many emotions, including sadness, anger, irritability, and frustration.
Give Us a Call...
Get In touch.
Ask Any Question.
AERCs Orangeville Location
873209 5 Line E, Orangeville, ON L9W 6A4
AERCs Toronto Location
1849 Yonge St, Floor 1, Suite 914, Toronto, ON M4S 1Y2
AERCs Mississauga Location
89 Queensway W #226, Mississauga, ON L5B 2V2
AERCS Partners With...

